At Maximize we discussed the topic of Enhancing the commercial maturity of your services business. In that conversation we spoke about ‘the Gap’. The Gap between your current service revenue and the maximum revenue you could achieve when every unit sold would have an associated ‘gold’ contract. This Gap is rather simple to calculate, and it won’t surprise me if the size of the Gap becomes a compelling reason to act.
The Gap
Why is it so important to acknowledge and quantify the Gap? If we don’t want to be like Alice in Wonderland, we need to know both our point of departure and the desired future state.
We see more and more service executives having a revenue growth target. In the grand scheme of both service transformation and margin contribution, this makes perfect sense. As much as it makes sense, a growth ambition of eg. 20% is ‘only’ directional and not linked to a potential. To make your service revenue growth ambition actionable you need handles; metrics to monitor, levers to pull. The benefit of defining the Gap is, it is SMARTspecific, measurable, actionable, realistic and time-bound).
Let me illustrate this with the analogy of market share. Suppose you say you want to grow your market share by 20%, it makes a huge difference if your current share is 10% or 70%.
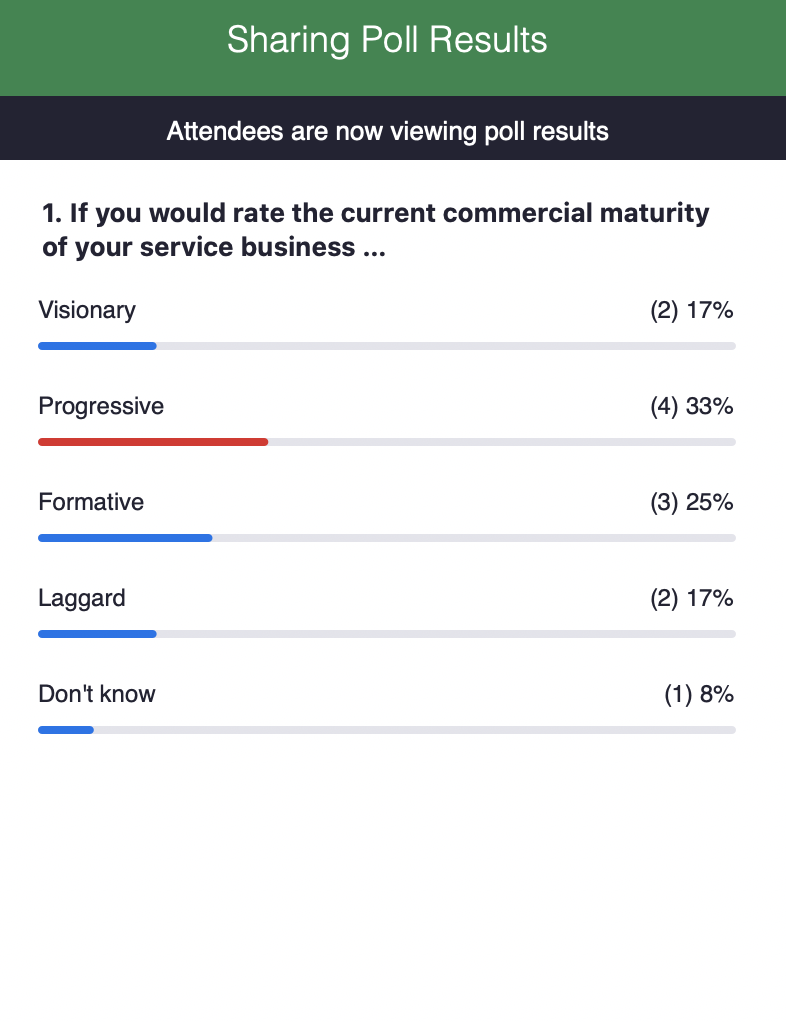
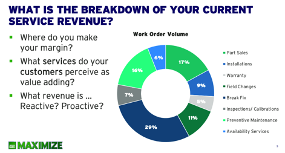
Where sales use market share, in the service domain we can use a blend of installed base visibility and attach rate. If you know where 50% of the units sold are installed, and of those units 60% have an associated service contract, you’re addressing 30% of the ‘market’. If those service contracts are a blend of warranty, bronze, silver and gold, your actual reach might be 15-20% of total addressable service market (TAM).
The above example is providing you with two things:
- A compelling reason to act
- Three mitigating handles
Compelling reason to Act
Let’s do some role play.
Suppose you are a service executive. You have a steady service revenue stream growing at the same rate of product sales. Your new management tasks you to grow faster than product sales, you need to grow your service revenue by 20%. What is your first response? How? Why 20%? The Gap will help you evaluate the feasibility of your new business objective. The Gap can also help you include other stakeholders in reaching your objectives. Think about sales leadership and portfolio development.
Suppose you are the sales leader. You work hard to maintain and grow market share. Growing market share by 20% is, to put it mildly, challenging. That challenge will only get bigger when your CFO changes the paradigm to margin contribution. To understand the dependency between sales and service I’ll flip to point-of-view towards the buyer of your product & services. From an asset owner’s perspective between 8-12%[1] of the life cycle cost are related to the purchase of the asset. The remainder is associated with maintenance and operational cost. This insight should trigger you and your CEO/CFO to rethink where you want to create your margin. It’s less about the one-time sale & margin of a product, and more about being able to create customer lock in throughout the life cycle of that product. Long-term contracts will deliver recurring revenue and margin contribution. The Gap is the quantification of what you are missing out on compared to a life cycle approach.
Suppose you are responsible for the product & services portfolio. Today you have a mix of warranty, bronze silver and gold. Each of those offerings has a different revenue/ margin contribution. Of course, you’d like all asset owners to buy your gold contract. The size of the Gap may be an indication to what extent your current portfolio aligns with the needs of the asset owners. Once you understand that an asset owner is more interested in using a product than owning it, your current service portfolio may need an upgrade.
Three mitigating handles
To mitigate the Gap, we’ve identified three handles:
- Installed Base Visibility
- Attach Rate
- Service offering
The first one, installed base visibility, builds on a variant of Peter Drucker’s quote “if you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it”. You need to know where your assets are, and in what condition to be able to sell associated services. The bigger the Gap, the bigger your motivation should be to invest in an asset life cycle database. Documenting the As-Built, As-Sold and As-Maintained. And yes, this may be more work when your organisation sells products through an indirect sales channel. The Gap may justify the investment.
The second and third handle go hand-in-hand. Once you have visibility of the installed units, you can start targeting those with your services portfolio. Important to realise, not the product specifications and characteristics are leading in the service offering, but the use-profile of that product. For the same product, wear and tear can be completely different, based on how the product is being used. This realisation emphasises the need to collect data throughout the operational life cycle of an asset. If sales says, ‘each touch point is an opportunity’, service can extend that paradigm with ‘each data point is an opportunity’.
Is it doable?
Absolutely! A target of 20% service revenue increase may sound abstract when you get it. In this blog we tried to break that task into manageable pieces. Standard service metrics will allow you to monitor installed base and attach rates. Introducing the Gap helps you to quantify your revenue growth potential. The Gap will create both the compelling reason to act and the arguments to convince other stakeholders to jointly work on this revenue growth target.
Please share your victories with us.
[1] Source: Insight… Accenture and total cost of ownership (2012)
This article is published in ServiceMax Field Service Digital on May 11th, 2021 and Field Technologies.